LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has emerged as a powerful tool in environmental conservation, offering detailed and accurate data that supports the protection and management of natural resources. By providing high-resolution, 3D mapping and analysis, LiDAR helps conservationists and environmental scientists monitor ecosystems, assess environmental changes, and implement effective conservation strategies. This article explores how LiDAR is enhancing environmental conservation and the benefits it brings to protecting our planet’s natural resources.
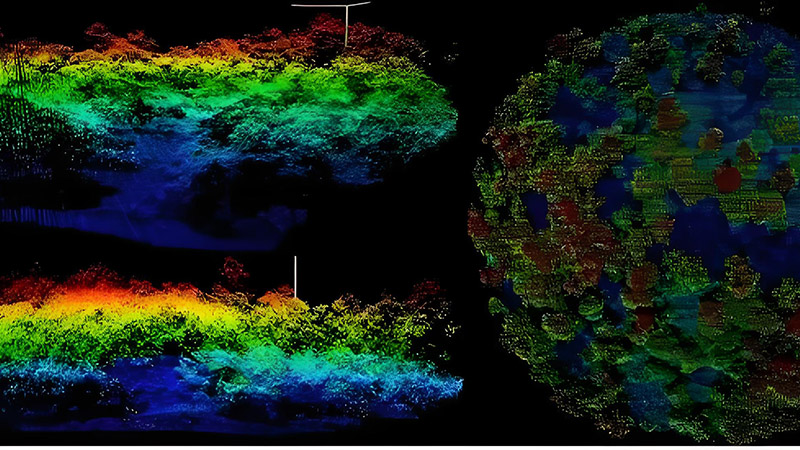
Mapping and Monitoring Ecosystems
One of the primary applications of LiDAR in environmental conservation is mapping and monitoring ecosystems. Traditional methods of assessing ecosystems can be limited by factors such as vegetation cover or challenging terrain, but LiDAR provides precise data that overcomes these limitations.
LiDAR technology captures detailed information about forest canopy structure, vegetation height, and land cover. This data is essential for mapping ecosystems, understanding habitat distribution, and monitoring changes over time. For example, LiDAR has been used to map tropical rainforests, track deforestation rates, and assess the health of coral reefs.
Assessing Habitat and Biodiversity
LiDAR plays a crucial role in assessing habitat quality and biodiversity. By providing detailed 3D models of vegetation and terrain, LiDAR helps identify critical habitats for wildlife and understand the spatial distribution of different species.
For example, LiDAR data can be used to analyze forest structure and canopy layers, which are important for various animal species. This information helps in identifying areas of high biodiversity, assessing the impact of habitat loss, and developing conservation strategies to protect endangered species and their habitats.
Detecting and Managing Environmental Changes
Environmental changes such as deforestation, land degradation, and climate change can have significant impacts on ecosystems and natural resources. LiDAR technology provides valuable data for detecting and managing these changes.
For example, LiDAR can be used to monitor changes in forest cover, track erosion and sedimentation, and assess the impact of land-use practices. By comparing LiDAR scans from different time periods, conservationists can detect changes in the environment, evaluate the effectiveness of conservation efforts, and implement adaptive management strategies.
Supporting Restoration and Rehabilitation Projects
Restoration and rehabilitation projects aim to restore degraded ecosystems and enhance environmental health. LiDAR technology supports these projects by providing detailed information on the current state of the environment and helping to plan and monitor restoration activities.
For example, LiDAR data can be used to identify areas that require reforestation, assess the success of planting efforts, and monitor changes in vegetation cover. This information helps in designing effective restoration strategies, tracking progress, and ensuring that restoration goals are met.
Managing Protected Areas and Reserves
Protected areas and nature reserves play a critical role in conserving biodiversity and preserving natural habitats. LiDAR technology aids in managing these areas by providing accurate data on land cover, terrain, and infrastructure.
LiDAR can be used to map protected areas, monitor changes in land use, and assess the impact of human activities. This information helps in enforcing protection measures, planning conservation activities, and ensuring that protected areas continue to provide habitat for wildlife and support ecosystem functions.
Enhancing Climate Change Research
Climate change has profound effects on ecosystems and natural resources. LiDAR technology contributes to climate change research by providing data on environmental changes and assessing the impact of climate-related factors.
For example, LiDAR can be used to measure changes in ice cover, monitor sea-level rise, and analyze shifts in vegetation patterns. This information helps researchers understand the effects of climate change on ecosystems, predict future changes, and develop strategies to mitigate and adapt to its impacts.
Improving Water Resource Management
Water resources are essential for ecosystems and human use, and LiDAR technology supports their management by providing detailed data on hydrology and water quality.
LiDAR can be used to map river channels, assess flood risks, and monitor changes in wetlands. This information helps in planning and managing water resources, implementing flood control measures, and protecting aquatic habitats. LiDAR data also supports the assessment of water quality and the identification of potential pollution sources.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of LiDAR in environmental conservation is promising, with ongoing advancements driving new applications and capabilities. Innovations include the development of more advanced LiDAR sensors, integration with other remote sensing technologies, and improvements in data processing and analysis.
For example, the integration of LiDAR with satellite imagery and drone technology will enhance the ability to capture data from large and remote areas. Advances in machine learning and data analytics will also improve the interpretation of LiDAR data, providing deeper insights into environmental conditions and trends.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology has become a valuable tool in environmental conservation, offering detailed and accurate data that supports the protection and management of natural resources. From mapping ecosystems and assessing biodiversity to detecting environmental changes and supporting restoration projects, LiDAR provides significant benefits for conservation efforts. As technology continues to evolve, LiDAR will play an increasingly important role in safeguarding our planet’s ecosystems and ensuring a sustainable future.


