LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has transformed the agricultural sector by providing high-resolution, 3D data that enhances crop management and supports precision farming. By offering detailed insights into field conditions, crop health, and terrain, LiDAR helps farmers make informed decisions, optimize resource use, and improve overall agricultural productivity. This article explores how LiDAR is revolutionizing agriculture and the benefits it brings to modern farming practices.
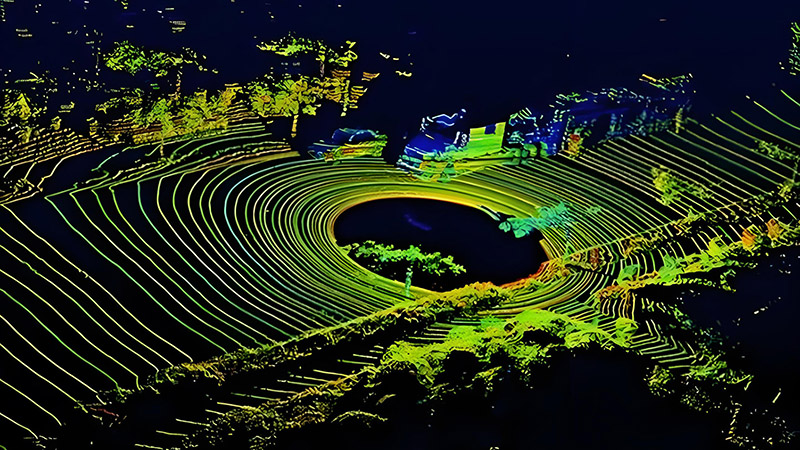
Detailed Crop and Field Mapping
One of the primary applications of LiDAR in agriculture is creating detailed maps of fields and crops. Traditional mapping methods can be limited by factors such as field size or crop density, but LiDAR provides precise, high-resolution data that overcomes these challenges.
LiDAR technology captures detailed information about the topography, crop height, and field layout. This data is essential for creating accurate maps that help farmers understand field conditions, plan planting and harvesting activities, and manage resources effectively. For example, LiDAR can reveal variations in crop height and density, which can be used to assess crop health and identify areas that may require additional attention.
Precision Farming and Resource Optimization
Precision farming involves using data-driven approaches to optimize agricultural practices and improve crop yields. LiDAR plays a crucial role in precision farming by providing accurate data that helps farmers make informed decisions about resource use and field management.
For instance, LiDAR data can be used to create detailed elevation models of fields, which are essential for designing efficient irrigation systems and managing water resources. By understanding the terrain and identifying areas prone to waterlogging or erosion, farmers can implement targeted irrigation practices that reduce water wastage and improve crop growth.
Monitoring Crop Health and Growth
LiDAR technology is valuable for monitoring crop health and growth throughout the growing season. By capturing data on crop height and canopy structure, LiDAR helps farmers assess the health of their crops and identify potential issues such as nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations.
For example, LiDAR can be used to analyze changes in crop height over time, providing insights into growth patterns and detecting anomalies. This information allows farmers to take timely actions, such as adjusting fertilization or applying pest control measures, to ensure optimal crop health and yield.
Assessing Soil Conditions and Management
Soil conditions play a critical role in crop growth and productivity. LiDAR technology supports soil management by providing detailed information about soil properties and terrain.
LiDAR data can be used to create detailed soil maps that reveal variations in soil texture, moisture levels, and compaction. This information helps farmers understand the soil conditions in different parts of their fields and implement targeted soil management practices. For example, farmers can use LiDAR data to identify areas with poor drainage and apply soil amendments or adjust cultivation practices to improve soil health.
Supporting Precision Harvesting
Harvesting is a critical stage in the agricultural cycle, and LiDAR technology supports precision harvesting by providing accurate data on crop distribution and maturity.
LiDAR can be used to create detailed maps of crop density and distribution, helping farmers plan harvesting operations more efficiently. By understanding the spatial variation in crop maturity, farmers can optimize harvest schedules and reduce losses. Additionally, LiDAR data helps in planning the layout of harvesting equipment and routes, leading to more efficient and less disruptive harvesting operations.
Enhancing Farm Management and Decision-Making
Farm management involves making a wide range of decisions related to crop production, resource use, and financial planning. LiDAR technology enhances farm management by providing accurate, real-time data that supports informed decision-making.
For example, LiDAR data can be integrated with other agricultural data sources, such as weather forecasts and yield estimates, to create comprehensive farm management plans. By analyzing LiDAR data alongside other information, farmers can make more accurate predictions, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall farm performance.
Improving Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is an important consideration in modern agriculture, and LiDAR technology contributes by providing data that supports sustainable practices and reduces environmental impact.
LiDAR can be used to monitor land use changes, assess the impact of agricultural practices on natural habitats, and manage soil erosion. By providing detailed information on field conditions and terrain, LiDAR helps farmers implement practices that minimize environmental impact, such as reducing soil erosion, managing runoff, and protecting natural resources.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of LiDAR in agriculture is promising, with ongoing advancements driving new applications and capabilities. Innovations include the development of more advanced and cost-effective LiDAR sensors, integration with drone technology, and improvements in data processing and analysis.
For example, drone-based LiDAR systems offer the ability to capture data from large and complex fields more efficiently. Integration with machine learning algorithms and real-time data analytics will enhance the ability to analyze and interpret LiDAR data, providing even more insights into crop management and precision farming.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology has revolutionized agriculture by providing detailed, high-resolution data that enhances crop management and supports precision farming. From mapping fields and optimizing resource use to monitoring crop health and supporting sustainable practices, LiDAR offers significant benefits for modern farming. As technology continues to advance, LiDAR will play an increasingly important role in driving agricultural innovation and improving productivity.


