Cave mapping is a critical aspect of speleology, the scientific study of caves. It involves creating detailed maps of cave systems, which are essential for scientific research, conservation, and exploration. As technology evolves, the techniques for cave mapping have become more sophisticated, allowing for greater precision and detail. This article explores the methods and significance of cave mapping, highlighting its importance in understanding and preserving subterranean environments.
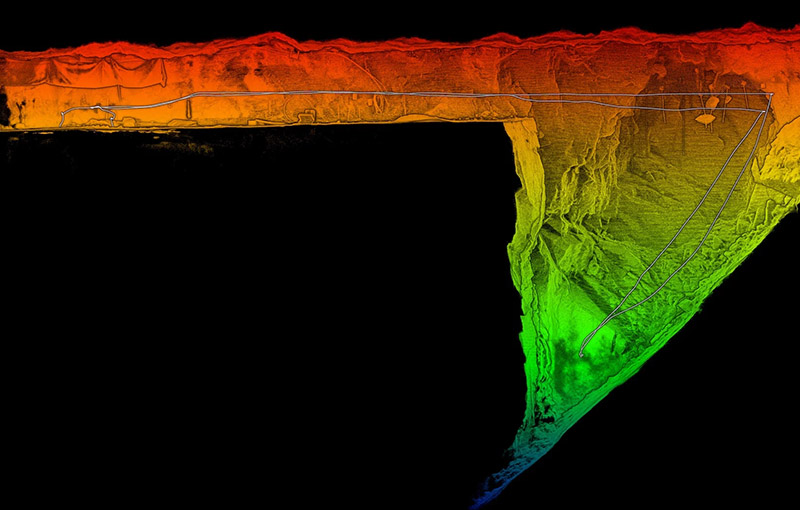
The Basics of Cave Mapping
Cave mapping involves documenting the physical layout of a cave system, including its passages, chambers, and geological features. Traditional methods include survey techniques using tape measures, compasses, and clinometers to record measurements and angles. These measurements are then used to create two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) maps of the cave.
Surveying a cave requires careful planning and execution. Survey teams often work in challenging conditions, including low visibility, confined spaces, and varying temperatures. Accurate measurements and detailed recordings are crucial for creating a comprehensive map that reflects the cave’s true layout.
Modern Techniques and Technologies
Advancements in technology have significantly improved cave mapping methods. One of the most notable innovations is the use of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology. LiDAR systems can scan cave interiors with laser pulses, generating high-resolution 3D models of the cave’s structure. This method provides unparalleled accuracy and detail, capturing features that might be missed with traditional techniques.
Another technological advancement is the use of photogrammetry, which involves taking overlapping photographs of the cave and using software to create 3D models. This technique is particularly useful for mapping intricate details and textures, such as mineral formations and cave art.
Applications of Cave Maps
Cave maps serve a variety of purposes beyond exploration. For scientists, they provide valuable data for studying geology, hydrology, and biology. Understanding the layout of a cave system can reveal information about its formation, the movement of groundwater, and the distribution of unique cave-dwelling species.
Conservationists use cave maps to identify and protect sensitive areas within caves. Accurate mapping helps in managing human activity, preventing damage to fragile formations, and preserving ecosystems. Additionally, cave maps are used in education and outreach, helping to raise awareness about the importance of cave conservation.
Challenges in Cave Mapping
Despite technological advancements, cave mapping remains a challenging task. Caves are often located in remote or difficult-to-access areas, requiring specialized equipment and expertise. Additionally, the dynamic nature of caves, with ongoing geological processes and shifting sediment, can complicate mapping efforts.
Safety is another concern, as cave environments can be hazardous. Mapping teams must be well-prepared for potential risks, including structural instability, flooding, and limited visibility. Proper training and equipment are essential for ensuring the safety of those involved in cave mapping.
The Future of Cave Mapping
The future of cave mapping is likely to be shaped by continued advancements in technology. Emerging tools, such as autonomous drones and advanced imaging techniques, hold promise for further improving mapping accuracy and efficiency. These innovations may allow for more detailed and comprehensive exploration of previously inaccessible cave systems.
Furthermore, increased collaboration between scientists, conservationists, and technology developers will enhance the understanding and preservation of cave environments. By leveraging new technologies and sharing knowledge, the field of cave mapping will continue to evolve, providing valuable insights into the hidden worlds beneath our feet.
Conclusion
Cave mapping is a vital component of speleology, offering insights into the structure, formation, and conservation of cave systems. As technology advances, cave mapping techniques become more sophisticated, providing greater detail and accuracy. By combining traditional methods with modern innovations, scientists and explorers can continue to unravel the mysteries of the subterranean world and contribute to the preservation of these unique environments.


