LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology is transforming industrial automation by providing advanced obstacle detection and avoidance capabilities. Through precise 3D mapping, LiDAR enhances safety and efficiency in various industrial applications, from autonomous vehicles to robotic systems.
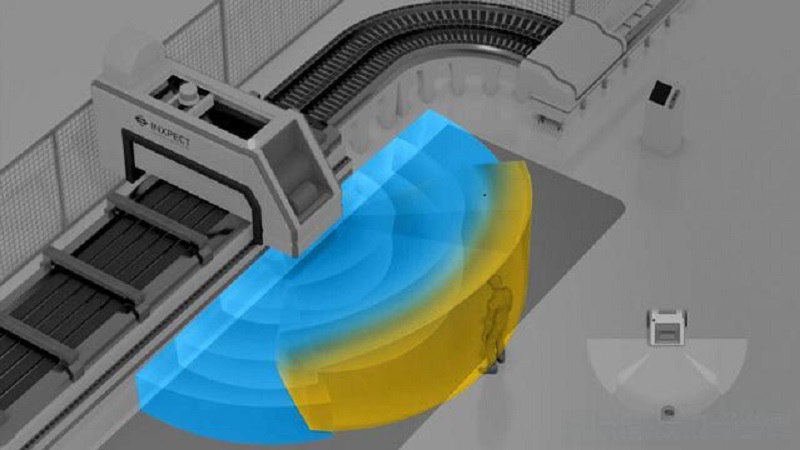
LiDAR operates by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for these pulses to bounce back from objects in the environment. This time-of-flight measurement is used to calculate the distance to each object, creating a detailed 3D map of the surroundings. This high-resolution data is crucial for detecting and avoiding obstacles in real-time.
Applications in Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, LiDAR is integrated into various automated systems to improve safety and efficiency. For example, autonomous forklifts and AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) use LiDAR to navigate complex environments such as warehouses and manufacturing floors. These vehicles can detect obstacles like shelves and other machinery, allowing them to adjust their path and avoid collisions.
Robotic arms equipped with LiDAR can also perform tasks such as material handling and assembly while avoiding obstacles. The precise spatial data provided by LiDAR enables these robots to interact with their environment effectively, reducing the risk of errors and equipment damage.
Advantages of LiDAR
One of the primary advantages of LiDAR is its ability to provide accurate, real-time data regardless of lighting conditions. Unlike traditional vision-based systems, LiDAR is not affected by darkness or glare, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments. Additionally, LiDAR’s high-resolution mapping allows for precise obstacle detection, enhancing the overall safety of automated systems.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its benefits, integrating LiDAR into industrial systems can present challenges. High computational demands for real-time data processing and the cost of LiDAR sensors can be significant. However, advancements in computing technology and sensor miniaturization are addressing these issues, making LiDAR more accessible and efficient.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology is revolutionizing industrial obstacle avoidance by providing accurate and reliable 3D mapping. Its applications in autonomous vehicles and robotic systems are enhancing safety and operational efficiency, making it a valuable tool in modern industrial automation.


