Real-time decision-making is a critical component of autonomous vehicle operation. For self-driving cars to navigate safely and efficiently, they must make rapid and accurate decisions based on real-time data from their surroundings. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology plays a significant role in this process by providing precise and timely environmental information. This article explores how LiDAR contributes to real-time decision-making in autonomous vehicles and the impact it has on overall performance and safety.
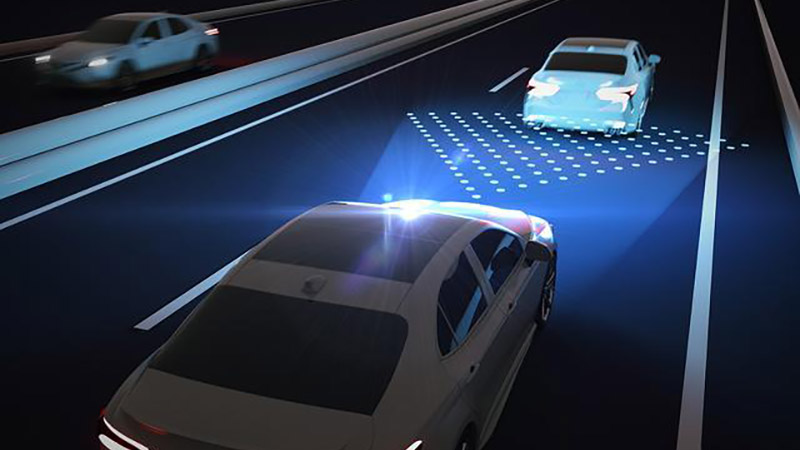
The Role of LiDAR in Real-Time Perception
1. High-Resolution Environmental Mapping
LiDAR generates high-resolution 3D maps of the vehicle’s surroundings by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for them to return after reflecting off objects. This detailed mapping provides a comprehensive view of the environment, including the positions and distances of objects, road features, and potential obstacles. The high-resolution data enables the vehicle’s autonomous system to perceive its environment with great accuracy, which is essential for making informed decisions.
2. Instantaneous Object Detection
LiDAR’s ability to provide real-time data is crucial for detecting and tracking objects in the vehicle’s path. As the vehicle moves, LiDAR continuously scans the environment, detecting objects such as pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles. This real-time object detection allows the autonomous system to assess potential hazards and make quick decisions to avoid collisions or other safety issues.
3. Dynamic Scene Analysis
The dynamic nature of driving environments requires the vehicle to analyze and respond to changing conditions rapidly. LiDAR’s real-time data allows the autonomous system to monitor the movement of objects and changes in the environment, such as traffic flow or the appearance of new obstacles. This dynamic scene analysis enables the vehicle to adapt its behavior in response to evolving situations, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Decision-Making Scenarios Enabled by LiDAR
1. Collision Avoidance
One of the most critical decision-making scenarios in autonomous driving is collision avoidance. LiDAR provides the real-time data needed to detect obstacles and assess their proximity. If an object suddenly appears in the vehicle’s path, LiDAR’s precise distance measurements enable the system to determine the best course of action, such as braking, steering, or changing lanes, to avoid a collision.
2. Navigation and Path Planning
Effective navigation and path planning are essential for autonomous vehicles to follow routes and reach destinations safely. LiDAR’s high-resolution environmental mapping helps the vehicle understand the layout of roads, intersections, and lane markings. This information allows the vehicle to plan its route, navigate turns, and handle complex driving scenarios, such as merging onto highways or navigating through intersections.
3. Traffic and Intersection Management
Navigating through traffic and intersections requires the vehicle to make decisions based on the behavior of other road users and traffic signals. LiDAR helps the vehicle detect and track the positions of vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists, as well as the status of traffic signals. This information enables the vehicle to make informed decisions about when to stop, yield, or proceed through an intersection, ensuring smooth and safe interactions with other road users.
4. Emergency Response
In emergency situations, such as sudden braking or evasive maneuvers, the vehicle must respond quickly and accurately. LiDAR’s real-time data allows the autonomous system to detect and assess the emergency situation, such as a vehicle braking suddenly in front of it or a pedestrian running into the road. The system can then execute the appropriate response, such as rapid braking or swerving, to mitigate the risk of an accident.
Integrating LiDAR with Other Sensors for Enhanced Decision-Making
While LiDAR provides valuable real-time data, it is often used in combination with other sensors, such as cameras and radar, to create a more comprehensive perception system. Sensor fusion combines data from multiple sources to improve the accuracy and reliability of decision-making.
Cameras: Cameras provide detailed visual information, such as color and texture, which complements the depth information from LiDAR. Together, they enhance object recognition and classification, contributing to more informed decision-making
Radar: Radar systems provide distance measurements and speed information, which can be used alongside LiDAR data to assess the movement and behavior of objects. This integration improves the vehicle’s ability to anticipate and respond to dynamic situations.
Conclusion
LiDAR plays a crucial role in real-time decision-making for autonomous vehicles by providing high-resolution environmental mapping, instantaneous object detection, and dynamic scene analysis. Its contribution to collision avoidance, navigation, traffic management, and emergency response enhances the overall performance and safety of autonomous driving systems. By integrating LiDAR with other sensors, autonomous vehicles can achieve more accurate and reliable decision-making, paving the way for safer and more efficient self-driving technology.


