In the realm of autonomous vehicles, sensing technology plays a critical role in enabling safe and efficient navigation. Two of the most prominent sensor types used are LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and camera systems. Each technology has its strengths and limitations, and understanding their comparative advantages is essential for developing effective autonomous driving systems. This article provides a comparative analysis of LiDAR and camera systems in the context of autonomous vehicles.
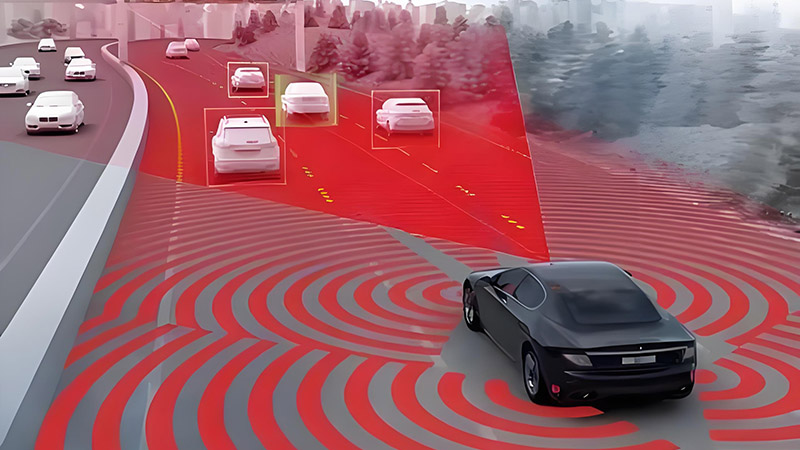
LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances to objects, creating a detailed 3D map of the environment. It is renowned for its high accuracy and precision in distance measurement, providing a comprehensive view of the surroundings.
Advantages of LiDAR
Precision and Accuracy: LiDAR provides highly accurate distance measurements and precise 3D mapping. This allows for detailed spatial awareness and accurate object detection, which is crucial for safe navigation and collision avoidance.
Performance in Low Light and Adverse Weather: LiDAR operates effectively in low light conditions and can perform well in adverse weather, such as fog or rain, where camera systems may struggle. The technology’s reliance on laser pulses rather than visible light makes it less affected by changes in lighting conditions.
Depth Perception: LiDAR’s ability to provide depth information is a significant advantage for detecting and measuring distances to objects. This capability allows autonomous vehicles to understand the spatial arrangement of objects in their environment.
Limitations of LiDAR
Cost: LiDAR systems can be expensive, especially high-performance models with long-range capabilities. The cost of LiDAR technology has been a barrier to its widespread adoption in consumer vehicles, although prices are gradually decreasing.
Data Volume: LiDAR generates large volumes of data, which require significant computational power to process. Managing and analyzing this data in real-time can be challenging and may require advanced hardware.
Limited Color Information: While LiDAR provides accurate distance measurements, it lacks color information, which can be important for recognizing and classifying objects. For example, differentiating between a red stop sign and a red traffic light may be challenging for LiDAR alone.
Camera Systems Overview
Camera systems use visual sensors to capture images and video of the vehicle’s surroundings. Cameras provide detailed visual information, including color and texture, which is valuable for object recognition and scene interpretation.
Advantages of Camera Systems
Rich Visual Information: Cameras capture detailed visual data, including color and texture, which is essential for recognizing and interpreting objects. This capability helps in identifying road signs, traffic lights, and various road markings.
Cost-Effectiveness: Camera systems are generally more affordable than LiDAR, making them a cost-effective option for autonomous vehicles. They are widely used in driver-assistance systems and are often integrated into existing vehicle designs.
Wide Field of View: Cameras can provide a broad field of view, which is beneficial for detecting objects and monitoring the environment. Multiple cameras can be used to achieve 360-degree coverage around the vehicle.
Limitations of Camera Systems
Performance in Adverse Conditions: Cameras can struggle in low light, glare, and adverse weather conditions. Visibility can be significantly reduced in fog, heavy rain, or at night, impacting the camera’s effectiveness in these scenarios.
Limited Depth Perception: Unlike LiDAR, cameras do not inherently provide depth information. Depth perception must be inferred from visual data, which can be less accurate and more computationally intensive than LiDAR-based depth measurements.
Dependence on Lighting Conditions: Camera performance is heavily dependent on lighting conditions. Changes in sunlight, shadows, and reflections can affect image quality and the camera’s ability to detect and recognize objects.
Complementary Use of LiDAR and Cameras
In practice, LiDAR and camera systems are often used together to leverage the strengths of each technology. Combining LiDAR’s precise depth information with cameras’ rich visual data provides a more comprehensive perception system. This sensor fusion approach enhances object detection, recognition, and scene understanding, leading to improved safety and performance.
1. Enhanced Object Recognition: Cameras can identify and classify objects based on visual characteristics, while LiDAR provides accurate distance measurements. Together, they create a more robust object recognition system.
2. Improved Environmental Understanding: LiDAR’s 3D mapping and cameras’ color information offer a complete view of the environment. This combination helps in interpreting complex driving scenarios and making informed decisions.
3. Redundancy and Reliability: Using both LiDAR and cameras provides redundancy, ensuring that if one system encounters limitations, the other can compensate. This improves the overall reliability of the autonomous driving system.
Conclusion
LiDAR and camera systems each have distinct advantages and limitations in the context of autonomous vehicles. LiDAR excels in precision, accuracy, and performance in adverse conditions, while cameras provide rich visual information and cost-effectiveness. The complementary use of both technologies offers a comprehensive and reliable approach to autonomous driving, enhancing safety and performance. As technology continues to advance, the integration of LiDAR and cameras will play a crucial role in the development of effective and safe autonomous vehicles.


