LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has revolutionized archaeology by providing detailed, three-dimensional data that enhances the discovery, documentation, and analysis of ancient sites and historical landscapes. By offering precise information on terrain, structures, and vegetation, LiDAR supports more efficient archaeological research, reveals previously hidden sites, and provides insights into past civilizations. This article explores how LiDAR is transforming archaeology and the benefits it brings to the field.
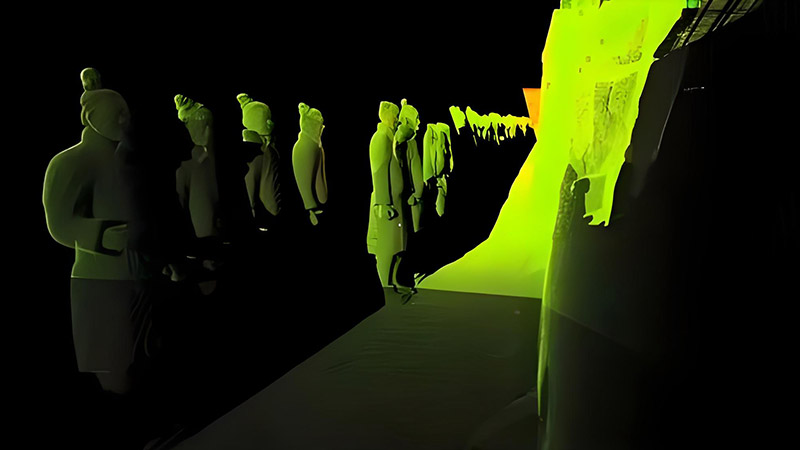
Revealing Hidden Archaeological Sites
One of the most significant contributions of LiDAR to archaeology is its ability to reveal hidden or obscured archaeological sites. Traditional archaeological surveys can be limited by dense vegetation, uneven terrain, or the sheer scale of the area being studied. LiDAR technology overcomes these challenges by penetrating through vegetation and providing a clear view of the underlying terrain.
LiDAR data captures detailed topographic information, creating high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) that reveal subtle features on the landscape. For example, LiDAR has been used to uncover ancient structures, such as cities, roads, and agricultural terraces, that were previously hidden beneath dense forest canopies. Notable discoveries, such as the ancient Maya city of Caracol in Belize and the lost city of Angkor in Cambodia, were made possible by LiDAR technology.
Mapping and Analyzing Ancient Landscapes
LiDAR technology is highly effective for mapping and analyzing ancient landscapes, providing valuable insights into how past civilizations interacted with their environments. LiDAR data offers a detailed view of historical landscapes, including changes in terrain, land use, and settlement patterns.
By creating accurate 3D models of ancient landscapes, archaeologists can study the spatial organization of settlements, roads, and agricultural systems. For example, LiDAR surveys have revealed intricate networks of ancient irrigation systems, trade routes, and ceremonial centers. This information helps researchers understand how ancient societies managed their resources, organized their communities, and adapted to environmental changes.
Supporting Site Documentation and Preservation
Documenting and preserving archaeological sites is a critical aspect of archaeological research, and LiDAR technology supports these efforts by providing precise and comprehensive data. LiDAR surveys create detailed records of site topography and features, which are essential for documenting site conditions and planning preservation strategies.
LiDAR data can be used to create accurate maps and 3D models of archaeological sites, capturing information on structures, artifacts, and site layout. This documentation is valuable for preserving historical records, planning conservation efforts, and supporting future research. For example, LiDAR data can be used to monitor changes in site conditions over time, assess the impact of environmental factors, and guide restoration efforts.
Enhancing Survey Efficiency and Coverage
LiDAR technology enhances survey efficiency and coverage by providing comprehensive data over large areas. Traditional archaeological surveys can be time-consuming and limited in scope, especially in challenging terrains or extensive regions. LiDAR surveys offer a more efficient and effective approach by covering large areas quickly and accurately.
LiDAR data can be collected from aerial platforms, such as aircraft or drones, allowing for extensive surveys of archaeological landscapes. This approach supports the identification of potential sites, the assessment of site density, and the prioritization of areas for detailed investigation. For example, LiDAR surveys can cover thousands of hectares in a fraction of the time required for ground-based surveys, providing a broader and more detailed view of the landscape.
Assisting in Excavation Planning and Research
LiDAR technology supports excavation planning and research by providing detailed information on site features and spatial relationships. Accurate 3D models of archaeological sites help researchers plan excavation strategies, identify key areas for investigation, and understand site layout.
LiDAR data can be used to visualize the distribution of artifacts, structures, and features, guiding excavation efforts and improving research outcomes. For example, LiDAR surveys can reveal the location of buried structures, such as walls or foundations, which can be targeted during excavation. This information helps archaeologists make informed decisions about where to dig and how to interpret the findings.
Revealing Settlement Patterns and Social Organization
Understanding settlement patterns and social organization is a key focus of archaeological research, and LiDAR technology provides valuable insights into these aspects. LiDAR data offers a detailed view of ancient settlements, including the layout of buildings, streets, and public spaces.
By analyzing LiDAR data, researchers can study the spatial organization of ancient cities and communities, revealing patterns of social organization, economic activity, and political structure. For example, LiDAR surveys have shown how ancient cities were organized into distinct neighborhoods, with specialized areas for trade, industry, and residential life. This information helps archaeologists reconstruct the social and economic dynamics of past civilizations.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of LiDAR in archaeology is promising, with ongoing advancements driving new applications and capabilities. Innovations include the development of more advanced LiDAR sensors, integration with other remote sensing technologies, and improvements in data processing and analysis.
For example, the integration of LiDAR with hyperspectral imaging and ground-penetrating radar (GPR) can provide a more comprehensive view of archaeological sites, combining information on surface features with insights into subsurface conditions. Advances in data processing and machine learning will enhance the ability to interpret LiDAR data, supporting more detailed and accurate archaeological research.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology has transformed archaeology by providing detailed, high-resolution data that enhances the discovery, documentation, and analysis of ancient sites and historical landscapes. From revealing hidden archaeological sites and mapping ancient landscapes to supporting site preservation and excavation planning, LiDAR offers significant benefits for modern archaeological research. As technology continues to evolve, LiDAR will play an increasingly important role in uncovering the secrets of the past and advancing our understanding of human history.


