Archaeology is a field dedicated to uncovering and understanding the past, and 3D LiDAR technology has become an invaluable tool in this endeavor. By providing precise and detailed three-dimensional data, 3D LiDAR helps archaeologists explore, document, and analyze ancient sites with unprecedented accuracy.
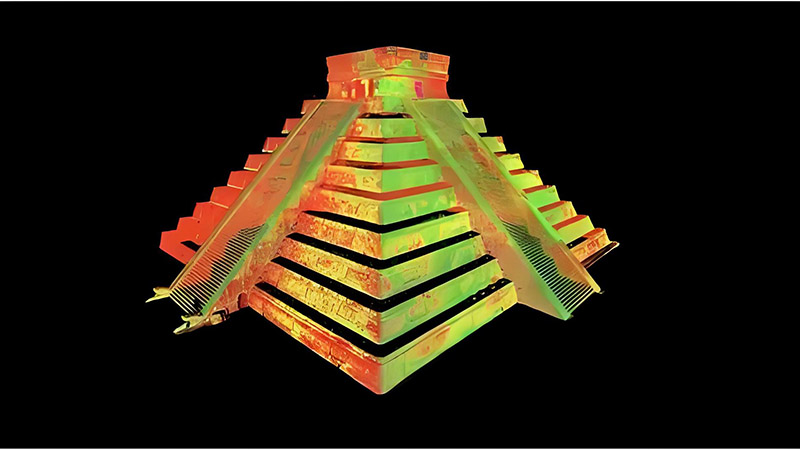
Revealing Hidden Structures
One of the most significant contributions of 3D LiDAR to archaeology is its ability to reveal hidden or obscured structures. LiDAR’s laser pulses can penetrate vegetation and ground cover to capture detailed data of underlying features. This is particularly useful in dense forests or overgrown sites where traditional excavation methods may not be feasible.
For example, LiDAR has been instrumental in discovering previously unknown ancient cities and architectural features buried beneath thick jungle canopies or sediment layers. This technology has led to significant archaeological discoveries, such as the identification of complex urban networks in places like the Maya lowlands.
Creating Detailed Site Models
3D LiDAR enables the creation of highly detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, providing a comprehensive view of the terrain and structures. These models can be used to study the spatial arrangement of artifacts, buildings, and other features, offering insights into ancient societies’ layout and organization.
These detailed models also serve as valuable records for future research and preservation efforts. By documenting sites in 3D, archaeologists create accurate digital archives that can be studied and shared without disturbing the physical site.
Enhancing Surveying and Mapping
In archaeological surveys, 3D LiDAR technology enhances the mapping and documentation of sites. Traditional surveying methods can be time-consuming and limited in their scope. LiDAR-equipped drones or ground-based scanners can rapidly survey large areas, generating precise maps that highlight significant features and help guide excavation efforts.
LiDAR data also allows archaeologists to analyze terrain changes and identify areas of interest for further investigation. By comparing historical and current LiDAR scans, researchers can track changes over time and gain insights into the evolution of ancient landscapes.
Supporting Conservation Efforts
3D LiDAR is not only useful for uncovering and documenting archaeological sites but also for their preservation. By providing detailed and accurate data, LiDAR helps in planning conservation strategies and managing site conditions. For instance, LiDAR data can identify areas at risk of erosion or damage, allowing for targeted conservation measures to protect and preserve these valuable cultural heritage sites.
Conclusion
3D LiDAR technology has revolutionized archaeology by providing precise, detailed, and non-invasive methods for exploring and documenting ancient sites. From revealing hidden structures to creating detailed site models and supporting conservation efforts, LiDAR plays a crucial role in understanding and preserving our shared human history.


